Revolutionising Industrial Product Design with FDM 3D Printing
From Concept to Small Batch Production
Industrial Product Design: Innovation, agility, and efficient workflows
In the fast-paced world of industrial product design, staying ahead of the competition requires innovation, agility, and efficient workflows. Traditional manufacturing methods often pose limitations in terms of cost, time, and customisation. However, the advent of FDM (Fused Deposition Modelling) 3D printing has revolutionised the landscape, offering exciting opportunities for proof of market prototyping and small batch production. In this article, we will take you on an exciting journey through a staged workflow, showcasing the seamless connection between industrial product design styling and FDM 3D printing.
Conceptualisation: Unleashing Creativity
The journey begins with the conceptualisation phase, where designers unleash their creativity to generate innovative ideas. Sketches, mood boards, and digital renderings play a pivotal role in visualising the product’s aesthetics and functionality. This stage sets the foundation for the subsequent steps, allowing designers to experiment and refine their concepts.
Images [below]: Designer’s sketchbook and digital renderings.
- 3D Printing – Engineering Sketch Concept Design
- 3D Printing – Product Sketch Concept Design
- 3D Printing – Automotive Sketch Concept Design
- 3D Printing – Product Design CAD Visualisation Production
- 3D Printing – Replacement / Reverse-Engineering improvement CAD Visualisation Production
- 3D Printing – Engineering CAD Visualisation Production
Images [above]: Designer working on a 3D Modelling software for producing 3D Print STL files.
3D Modelling: Transforming Ideas into Digital Reality
With the concept in hand, it’s time to translate it into a digital model. Using powerful CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software, designers meticulously create a 3D model that accurately captures the desired form, features, and dimensions of the product. This step enables precise visualisation and serves as the basis for the subsequent 3D printing process.
Images [below]: Fabrication of 3D STL files and 3D Prints into Prototypes.
- 3D Printing – Batch or Mass Production, Assembly, Manufacture.
- 3D Printing – Scientific/Electrical Production, Assembly, Manufacture.
- 3D Printing – Flexible Production, Assembly, Manufacture.
- 3D Printing – Engineering Production, Assembly, Manufacture.
- 3D Printing – Architectural Model Production, Assembly, Manufacture.
- 3D Printing – Museum/Reproduction Production, Assembly, Manufacture.
- 3D Printing – Point of Sale Production, Assembly, Manufacture.
- 3D Printing – Automotive Production, Assembly, Manufacture.
Optimisation for FDM Printing: Design for Success
Next, the 3D model is optimised for FDM printing. Designers take into account factors such as structural integrity, support structures, material usage, and printability. By leveraging the capabilities and limitations of FDM 3D printing, they ensure that the final product is manufacturable and retains the envisioned design aesthetics.
Images [below]: Models with optimised geometry for FDM printing.
- 3D Printing – Fluid Pump – Optimised for 3D Print production
- 3D Printing – Flexible Switch – Optimised for 3D Print production
- 3D Printing – Clamp Mechanism – Optimised for 3D Print production
- 3D Printing – Battery Cover – Optimised for 3D Print Production
- 3D Printing – Automotive Gearing – Optimised for 3D Print Production
- 3D Printing – Pharmaceutical/Medical – Optimised for 3D Print Production
- 3D Printing – Disability Assistive Items – Optimised for 3D Print Production
- 3D Printing – Health and Safety – Optimised for 3D Print Production
- 3D Printing – Museum Military – Optimised for 3D Print Production
- 3D Printing – Automotive Products – Optimised for 3D Print Production
- 3D Printing – Engineering Replacement Parts – Optimised for 3D Print Production
- 3D Printing – Custom Automotive Design Parts – Optimised for 3D Print Production
Proof of Market Prototyping: Tangible Validation
Once the optimised 3D model is ready, it’s time to bring it to life through FDM 3D printing. The selected 3D printer converts the digital design into physical reality, layer by layer. The beauty of FDM technology lies in its ability to rapidly prototype complex geometries and iterate designs quickly. With the physical prototype in hand, designers can assess the product’s form, fit, and function, making informed refinements.
Image/Video [below]: 3D Printers in action and Building the Prototype.
Industrial Product Design Refinement and Iteration:
Continuous Improvement
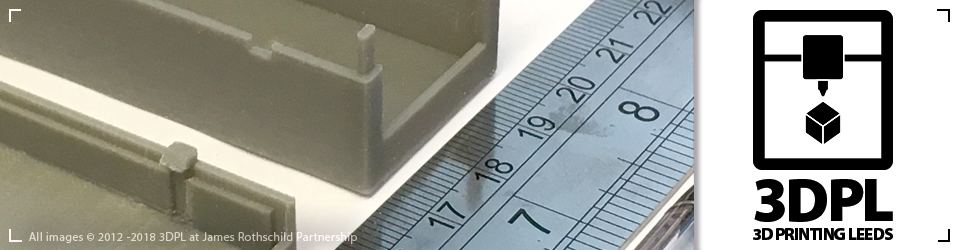
Based on feedback from the proof of market prototype, designers refine and iterate the design further. This iterative process allows for continuous improvement and ensures that the final product meets the desired specifications. The flexibility of FDM 3D printing enables designers to make design changes swiftly, reducing time-to-market and maximising innovation potential. (Image: Designer holding the prototype and making notes)
Industrial Product Design for 3D Printing – Prototype Measuring and Adjustments for Refinement and Innovation samples.
Small Batch Production: Scaling Innovation
With the design refined and validated, it’s time to move towards small batch production. FDM 3D printing excels in low-volume manufacturing, enabling cost-effective production of customised products without the need for expensive tooling or molds. By leveraging the scalability of 3D printing technology, designers can cater to niche markets, create limited editions, or even offer personalised products.
Images [below] : Array of identical products produced through FDM 3D printing.
- 3D Printing – Safety Whistle – Batch or Mass Product
- 3D Printing – Smoke Grenade INERT Dummy Base for Training – Batch or Mass Product
- 3D Printing – Slide Clips for a Flight Case – Batch or Mass Product
- 3D Printing – Floor Port Covers – Batch or Mass Product
Conclusion:
The integration of industrial product design styling with FDM 3D printing has ushered in a new era of creativity, speed, and cost-efficiency. By following the staged workflow outlined above, designers can unleash their imagination, validate their ideas through proof of market prototyping, iterate designs, and seamlessly transition to small batch production. The possibilities are endless, and the benefits are substantial.
To delve deeper into the world of industrial product design and FDM 3D printing, check out this informative article on the role of 3D printing in enhancing manufacturing processes. For insights into the latest trends and innovations in the industry, explore this insightful report on the future of additive manufacturing.
- Embrace the power of FDM 3D printing and witness the transformation of your product design ideas into reality.
- With enhanced speed, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness, this technology opens new doors for creativity, prototyping, and small batch production.
- Revolutionise your product development process and stay ahead in the competitive market with FDM 3D printing.
Remember, the future of industrial product design lies in the synergy between innovation and technology. Embrace the possibilities of FDM 3D printing and unlock a world of endless opportunities for your business.